The correct answer is explained below:
Step-by-step explanation:
- According to the question, photic sneezing and wet ear wax are dominant traits.
- The dominant and recessive alleles for photic sneezing is represented by P and p respectively.
- Therefore, PP and Pp genotype individuals are photic sneezing positive and pp genotype individuals are photic sneezing negative.
- The dominant and recessive alleles for wet ear wax is represented by E and e respectively.
- Therefore, EE and Ee genotype individuals have wet ear wax and ee genotype individuals have dry ear wax.
- The woman is said to be unaffected by photic sneezing and is heterozygous for wet ear wax, so her genotype would be ppEe.
- The gametes produced by the woman are: pE and pe.
- The man is said to be heterozygous for photic sneezing and has dry ear wax, so his genotype would be Ppee.
- The gametes produced by the man are: Pe and pe.
- Mating the man and the woman we get the following offspring,
pE pe
Pe PpEe Ppee
Photic sneezing/Ear wax Positive/Wet Positive/Dry
pe ppEe ppee
Photic sneezing/Ear wax Negative/Wet Negative/Dry
- The genotypes and the phenotypes of the offspring obtained by the mating is represented in the Punnett square shown above.
- The percentage of children who would sneeze when exposed to sunlight, that is, photic sneezing positive and have dry ear wax
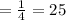 %.
%.