Answer:
The potential energy of the more massive one is twice that of the other.
Step-by-step explanation:
Potential energy is given by
PE = mgh
where m = mass of body, g = acceleration of gravity and h = height or elevation.
For the less massive car, let the mass be
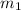 . Then its PE is
. Then its PE is
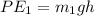
For the massive car, let the mass be
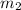 . Its PE is
. Its PE is
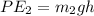
But
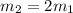
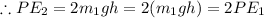
Hence, the potential energy of the more massive one is twice that of the other.