Answer : The ratio of the concentration of substance A inside the cell to the concentration outside is, 296.2
Explanation :
The relation between the equilibrium constant and standard Gibbs free energy is:
![\Delta G^o=-RT* \ln Q\\\\\Delta G^o=-RT* \ln (([A]_(inside))/([A]_(outside)))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/jfyfb04zslbl2idoa2tcuwkdi8z9pgplfp.png)
where,
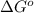 = standard Gibbs free energy = -14.1 kJ/mol
= standard Gibbs free energy = -14.1 kJ/mol
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/K.mol
T = temperature =
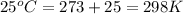
Q = reaction quotient
![[A]_(inside)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/94imzk9434guc16syk4nhaavl4ki2ug2ga.png) = concentration inside the cell
= concentration inside the cell
![[A]_(outside)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/8sqwbl91136232e1xakdoet1ortwqdct6x.png) = concentration outside the cell
= concentration outside the cell
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
![-14.1* 10^3J/mol =-(8.314J/K.mol)* (298K)* \ln (([A]_(inside))/([A]_(outside)))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/a4v8k26xr1lhmv55oizqyfz72wkqa5w8tw.png)
![([A]_(inside))/([A]_(outside))=296.2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/3rmmbk2tql6wri63qagt6se9wwlqkpaybr.png)
Thus, the ratio of the concentration of substance A inside the cell to the concentration outside is, 296.2