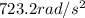Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The angular acceleration of an object in rotation is equal to the rate of change of its angular velocity.
Mathematically:
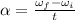
where
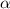 is the angular acceleration
is the angular acceleration
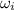 is the initial angular velocity
is the initial angular velocity
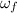 is the final angular velocity
is the final angular velocity
t is the time elapsed
For the optical disk in this problem, we have:
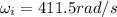 is the initial angular velocity
is the initial angular velocity
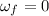 is the final angular velocity (because the disk comes to rest)
is the final angular velocity (because the disk comes to rest)
t = 0.569 s is the time elapsed
So, the angular acceleration is

And since we are only interested in the magnitude, then the magnitude is