The final temperature is -138 °C.
Step-by-step explanation:
Using the equation of specific heat
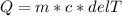
We can easily find the final temperature of a 73.174 g of copper sample. As we know that specific heat is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of the object to 1°C.
The specific heat of copper is known as 0.387 J/g°C and the initial temperature is said as 102 °C . The mass is given as 73.174 g. The heat released is 6800 J.
Since the heat is released the Q value will be negative.
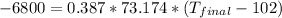
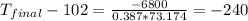
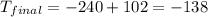
Thus, the final temperature is -138 °C.