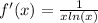Answer:
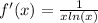
Explanation:
In order to solve this problem, we rewrite the original function as:
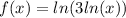
In order to find the derivative, we apply the chain rule for a composite function, which states that:
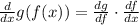
By applying the chain rule, we obtain the following:
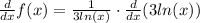 (1)
(1)
We also know that the derivative of the logarithm is
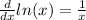
And since 3 is just a constant, expression (1) becomes:
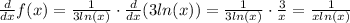
So, the derivative of the function is