Answer:
a) P(X < 14) = 0.0228.
b) 49 batteries must be tested.
Explanation:
To solve this question, we need to understand the normal probability distribution and the central limit theorem.
Normal probability distribution
Problems of normally distributed samples are solved using the z-score formula.
In a set with mean
 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
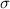 , the zscore of a measure X is given by:
, the zscore of a measure X is given by:
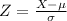
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X. Subtracting 1 by the pvalue, we get the probability that the value of the measure is greater than X.
Central Limit Theorem
The Central Limit Theorem estabilishes that, for a normally distributed random variable X, with mean
 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
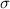 , the sampling distribution of the sample means with size n can be approximated to a normal distribution with mean
, the sampling distribution of the sample means with size n can be approximated to a normal distribution with mean
 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
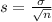 .
.
For a skewed variable, the Central Limit Theorem can also be applied, as long as n is at least 30.
In this problem, we have that:
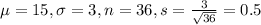
(a) If the claim is true, what is P(X < 14)?
This is the pvalue of Z when X = 14. So
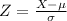
By the Central Limit Theorem
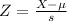
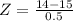
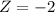
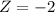 has a pvalue of 0.0228
has a pvalue of 0.0228
So
P(X < 14) = 0.0228.
(b) How many batteries must be tested so that the P(X < 14) = 0.01?
Now we want to find the size of the sample for which X = 14 is in the first percentile, that is, Z when X = 14 has a pvalue of 0.01. So it is Z = -2.327.
First we have to find the standard deviation of the sample in this case.
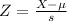
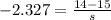
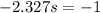
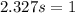
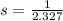
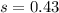
We know that
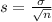
So
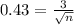
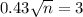
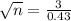
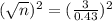
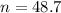
Rounding up
49 batteries must be tested.