Answer : The dissociation constant of the PFK‑inhibitor complex is, 5 µM
Explanation :
The expression for reversible competitive inhibition when apparent Km affected by addition of the inhibitor is:
![K_m_a=K_m[1+(I)/(K_i)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/biology/college/e2bnunaxi7iafqlqdr52dbm6x3pzl1x47r.png)
where,
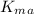 = apparent value = 52 µM
= apparent value = 52 µM
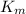 = Michaelis–Menten constant = 40 µM
= Michaelis–Menten constant = 40 µM
I = inhibitor concentration = 1.5 µM
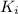 = dissociation constant of the PFK‑inhibitor complex
= dissociation constant of the PFK‑inhibitor complex
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
![52\mu M=40\mu M[1+(1.5\mu M)/(K_i)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/biology/college/pmj42qx0sg1euckt0qzsh0ujwp5htxvzcb.png)
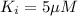
Therefore, the dissociation constant of the PFK‑inhibitor complex is, 5 µM