Answer:
= 8.33 Watt
Step-by-step explanation:
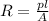
where,
p = resistivity
l = length
A = cross section area
Given that ,
p = resistivity = 6.0 × 10–8 Ω
l = 2m
A = cross section area = 2.0 mm × 2.0 mm = 4 x 10^-6 m^2
A = 2 x 2 mm^2 = 4 x 10^-6 m^2
p = 6 x 10^-8 ohm metre,
V = 0.5 V
Let R be the resistance of the rod
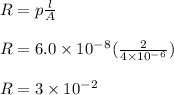
R = 3 × 10⁻²Ω
Heat generated = V^2 / R
= (0.5)^2 / (3 x 10^-2)
= 8.33 Watt