The firm’s marginal cost of production when the firm is producing 50 units of output is 33.33
Solution:
The production function is Q =
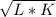
The initial value is 10 units. The production value is 50 units The manufacturing cycle needs work as stated below.
Q =
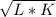
Q =
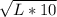
L =
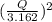
The wage rate is $15 . The following is the expense of the manufacturing process.
TC =
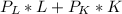
TC =
![( 15 * ((Q)/(3.162) )^(2) ) + [ P_(k * 10)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/business/college/tnydr5ngehyyq0rcx5x3kj24pkwj72bnzu.png)
The marginal production cost is really the increase in manufacturing costs as output increases by 1 point.
As listed below, the marginal cost:
TC =
![( 15 * ((Q)/(3.162) )^(2) ) + [ P_(k * 10)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/business/college/tnydr5ngehyyq0rcx5x3kj24pkwj72bnzu.png)
MC =
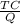 =
=
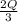
MC =
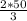 = 33.33
= 33.33