Answer:
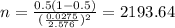
And rounded up we have that n=2194
Explanation:
Previous concepts
A confidence interval is "a range of values that’s likely to include a population value with a certain degree of confidence. It is often expressed a % whereby a population means lies between an upper and lower interval".
The margin of error is the range of values below and above the sample statistic in a confidence interval.
Normal distribution, is a "probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showing that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean".
The population proportion have the following distribution
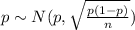
Solution to the problem
In order to find the critical value we need to take in count that we are finding the interval for a proportion, so on this case we need to use the z distribution. Since our interval is at 99% of confidence, our significance level would be given by
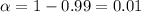 and
and
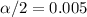 . And the critical value would be given by:
. And the critical value would be given by:
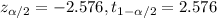
The margin of error for the proportion interval is given by this formula:
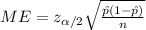 (a)
(a)
And on this case we have that
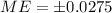 and we are interested in order to find the value of n, if we solve n from equation (a) we got:
and we are interested in order to find the value of n, if we solve n from equation (a) we got:
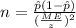 (b)
(b)
Since we don't have prior information for the true proportion we can use
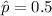 as an estimator. And replacing into equation (b) the values from part a we got:
as an estimator. And replacing into equation (b) the values from part a we got:
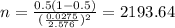
And rounded up we have that n=2194