Answer:
-241.826 kJ·mol⁻¹; -146.9 J·K⁻¹mol⁻¹; 664.6 J·K⁻¹mol⁻¹; spontaneous
Step-by-step explanation:
½O₂(g) + H₂(g) ⟶ H₂O(g)
ΔHf°/kJ·mol⁻¹: 0 0 -241.826
S°/J·K⁻¹mol⁻¹: 205.0 130.6 188.7
1. ΔᵣH
ΔᵣH = products -reactants = -241.826 -(0 + 0) = -241.826 kJ·mol⁻¹
2. ΔᵣS
ΔᵣS = products - reactants = 188.7 - (205.0 + 130.6) = 188.7 - 335.6 = -146.9 J·K⁻¹mol⁻¹
3. ΔS(univ)
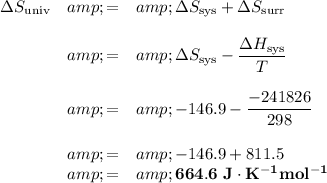
4. Spontaneity
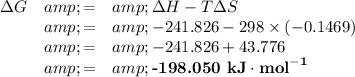
ΔG is negative, so the reaction is spontaneous.