Answer:
The concentrations of A, B, and C at equilibrium:
[A] = 0.0 M
[B] = 2.7 M
[C] = 2.4 M
Step-by-step explanation:
Concentration of 1.80 mol of A in 1.00 L container :
![[A]=(1.80 mol)/(1.00 L)=1.80 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/a96l9980odnfrrjluz8tp30wl1yad5e6ek.png)
Concentration of 3.90 mol of B in 1.00 L container :
![[B]=(3.90 mol)/(1.00 L)=3.90 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/8ech7dmui5lwwhdvvns2alekos33xxopjt.png)
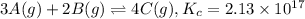
Initially
1.80 M 3.90 M 0
At equilibrium
(1.80-3x)M (3.90-2x) 4x
The expression of an equilibrium constant is given by :
![K_c=([C]^4)/([A]^3[B]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/42i7uwwujf2tqtwbhn8hkdpytlo323zpru.png)
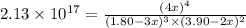
Solving for x:
x = 0.600
The concentrations of A, B, and C at equilibrium:
[A] = [1.80-3x]=[1.80-3 × 0.600]= 0 M
[B] = [3.90-2x] = [3.90-2 × 0.600] = 2.7 M
[C] = [4x] =[4 × 0.600 M] = 2.4 M