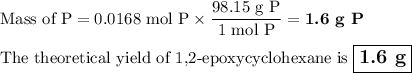Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Gather all the information in one place.
Mᵣ: 179.05 40 98.15
BrC₆H₁₀OH + NaOH ⟶ C₆H₁₀O + NaBr + H₂O
m/g: 3.0
V/mL: 25
C/%: 10
ρ/g·mL⁻¹ 1.11
Let's call BrC₆H₁₀OH "R" (reactant) and C₆H₁₀O "P" (product).
They have given us the amounts of two reactants and asked us to calculate the amount of product. This is a limiting reactant problem.
1. Calculate the moles of each reactant
(a) BrC₆H₁₀OH
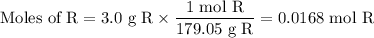
(b) NaOH
(i) Mass of solution
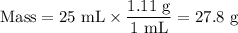
(ii) Mass of NaOH
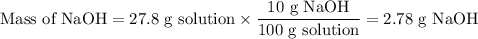
(iii) Moles of NaOH
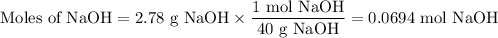
3. Calculate the moles of C₆H₁₀O you can obtain from each reactant
The molar ratios are all 1:1, so
(a) 0.0168 mol R ⟶ 0.0168 mol P
(b) 0.0694 mol NaOH ⟶ 0.0694 mol P
R is the limiting reactant, because it gives fewer moles of P.
3. Calculate the theoretical yield.