Answer:
High activation energy is the reason behind unsuccessful reaction.
Step-by-step explanation:
There are two types of reaction: (1) thermodynamically controlled reaction and (2) kinetically controlled reaction.
Thermodynamically controlled reaction are associated with change in enthalpy during reaction. More negative the enthalpy change, more favored will be the reaction.
Kinetically controlled reaction are associated with activation energy of a reaction. The lower the activation energy value, the more rapid will be the reaction.
Here, reaction between
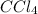 and
and
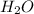 is thermodynamically favored due to negative enthalpy change but the high activation energy does not allow the reaction to take place by simple mixing.
is thermodynamically favored due to negative enthalpy change but the high activation energy does not allow the reaction to take place by simple mixing.