Answer:
The speed of the big fish after swallowing the small fish is 0.38 m/s.
Step-by-step explanation:
Consider west to east direction as positive and the opposite direction as negative.
Given:
Mass of big fish (m₁) = 12.0 kg
Initial velocity of big fish (u₁) = 75 cm/s = 0.75 m/s
Mass of small fish (m₂) = 1 kg
Initial velocity of small fish (u₂) = -4 m/s (Direction is opposite to u₁)
After swallowing the small fish, both the fishes move together with same velocity. Let the velocity be 'v'.
So, as there are no effects of drag or any other forces, the given scenario can be considered as a case of inelastic collision where the objects move together with same velocity after collision.
The momentum is conserved in inelastic collision. Therefore,
Initial momentum of the fishes = Final momentum of the fishes
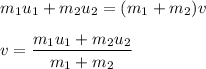
Now, plug in the given values and solve for 'v'. This gives,
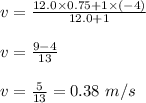
Therefore, the speed of the big fish after swallowing the small fish is 0.38 m/s