Step-by-step explanation:
For the given reaction:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
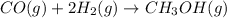
![Rate=k[CO]^x[H_2]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/jj8dqbhla3p48yi9ixefatvhrhwsllpha5.png)
where x and y are order wrt to
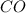 and
and
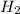
According to collision theory , the molecules must collide for a reaction to take place. According to collision theory , the rate of a reaction is proportional to rate of collision of reactants.
Thus with an increase in concentration of reactants , the rate of reaction also increases. This is because if the concentration of reactants increases , the chances of collision between molecules also increases and thus more products wil be formed which in turn increases the rate of reaction.