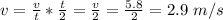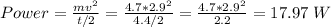Answer:
(a) work done is 79.054 J
(b) power at the end of the interval is 35.93 W
(c) power at the end of the first half of the interval is 17.97 W
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
mass of the object, m = 4.7 kg
final velocity, v = 5.8 m/s
time interval, t = 4.4 s
Part (a) work done on the object by the force accelerating it in 4.4 s interval
W = Fd = Δ KE
initial velocity, u = 0
W = ¹/₂mv²
W = ¹/₂ x 4.7 x (5.8)² = 79.054 J
Part (b) The instantaneous power due to that force at the end of the interval
Power = Fv
= mv/t x v
= mv²/t
= 4.7 x (5.8)² / 4.4
= 35.93 W
Part (c) power at first half of the interval
Power = Fv
velocity, v at half of t
v = u + at
v = at
t is half
v = a(t/2)
also a = v/t