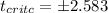Answer:
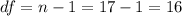
And for this case we want to find two critical values that accumulates 0.01 of the area on each tail, and we can use the t distribution table or Excel with the following codes:
"=T.INV(0.01,16)"
"=T.INV(1-0.01,16)"
And we got:
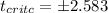
Explanation:
Previous concepts
The t distribution (Student’s t-distribution) is a "probability distribution that is used to estimate population parameters when the sample size is small (n<30) or when the population variance is unknown".
The shape of the t distribution is determined by its degrees of freedom and when the degrees of freedom increase the t distirbution becomes a normal distribution approximately.
The degrees of freedom represent "the number of independent observations in a set of data. For example if we estimate a mean score from a single sample, the number of independent observations would be equal to the sample size minus one."
Solution to the problem
For this case we want to do inference about the sample mean
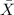
And for this case we can use the t distribution, the first step on this case is find the degrees of freedom given by:
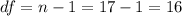
And for this case we want to find two critical values that accumulates 0.01 of the area on each tail, and we can use the t distribution table or Excel with the following codes:
"=T.INV(0.01,16)"
"=T.INV(1-0.01,16)"
And we got: