Answer:
Explanation:
Hello!
The objective is to compare the mean rating on the client satisfaction survey of two consultants A and B.
Consultant A
X₁: Rating on the client satisfaction survey given to consultant A
n₁= 16
X[bar]₁= 6.82
S₁= 0.64
Consultant B
X₂: Rating on the client satisfaction survey given to consultant B
n₂= 10
X[bar]₂= 6.25
S₂= 0.75
a. The claim is that consultant A, which is more experienced, has a higher average service rate than consultant B, which has less experience, then the hypotheses are:
H₀: μ₁ ≤ μ₂
H₁: μ₁ > μ₂
b. If both variables have a normal distribution and the population's variances are unknown but equal, the statistic for this test is a t-test for independent samples with pooled sample variance.
![t_(H_0)= \frac{(X[bar]_1-X[bar]_2)-(Mu_1-Mu_2)}{Sa*\sqrt{(1)/(n_1) +(1)/(n_2) } } ~~t_(n_1+n_2-2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/owa5uo1ylwrfjkkwzndvu22t7vjj6o7756.png)
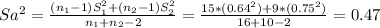
Sa= 0.68
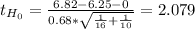
c. The p-value is the probability of obtaining a value as extreme as the value of the statistic. As the test it is one-tailed and has the same direction (right), symbolically:
P(t₂₄≥2.079)= 1 - P(t₂₄<2.079)= 1 - 0.9758= 0.0242
d. The p-value:0.0242 is less than α:0.05, then the decision is to reject the null hypothesis.
Using a significance level of 5%, there is significant evidence to say that the average service rate of consultant A is higher than the average service rate of consultant B.
I hope this helps!