Answer:
a) 129.14 g/mol
b) 8.87
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
mass of the ionic compound [NaA] = 18.08 g
Volume of water = 116.0 mL = 0.116 L
Let the mole of the acid HCl = 0.140 M
Volume of the acid = 500.0 mL = 0.500 L
pH = 4.63
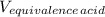 = 1.00 L
= 1.00 L
Equation for the reaction can be represented as:

From above; 1 mole of an ionic compound reacts with 1 mole of an acid to reach equivalence point = 0.140 M × 1.00 L
= 0.140 mol
Thus, 0.140 mol of HCl neutralize 0.140 mol of ionic compound at equilibrium
Thus, the molar mass of the sample =
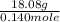
= 129.14 g/mol
b) since pH = pKa
Then pKa of HA = 4.63
Ka =
![10^{-4.63]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/mg43fdqll6q9zt1gki3lanty3kkhfvkrmi.png)
=
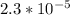
![[A^-]equ = (0.140M*1.00L)/(1.00L+0.116L)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/cdi2gb4ey1g6b3kiggaijswlqcoqknvakh.png)
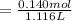
= 0.1255 M
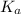 of HA =
of HA =
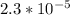
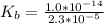
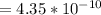
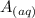 +
+
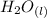
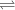
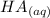 +
+
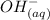
Initial 0.1255 0 0
Change - x + x + x
Equilibrium 0.1255 - x x x
![K_b = ([HA][OH^-])/([A^-])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/fed756otf6r3uu3cip6n6qbn3w2zut9xoa.png)
![4.35*10^(-10) = ([x][x])/([0.1255-x])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/3d4cllmnk9qw9j04uzo27a8lg2taf7ab9u.png)
As
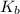 is very small, (o.1255 - x) = 0.1255
is very small, (o.1255 - x) = 0.1255
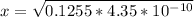
[OH⁻] =
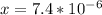
But pOH = - log [OH⁻]
= - log [
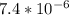 ]
]
= 5.13
pH = 14.00 = 5.13
pH = 8.87