Answer: Yes, it can be a single, ordinary star.
Explanation: To determine a mass of a star, we use the orbital speed formula, given by: v =
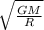 , where
, where
v is the speed;
G is a constant: G = 6.67*
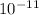
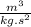
M is mass of a massive object;
R is the distance between the object orbiting and the massive object;
The formula can be rewritten as:
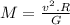
First, we change R from light years to km:
1km=1.057*
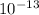
R=
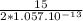
Calculating mass:
M =
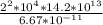
M = 4.25*
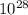 kg
kg
A solar mass is the standard unit of mass. It is approximately 2*
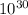 Kg and can be used for comparison: A single star cannot be more than 50 solar masses.
Kg and can be used for comparison: A single star cannot be more than 50 solar masses.
50 solar masses = 50*2*
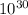 =
=
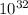 kg
kg
Comparing the mass of the object with this parameter, we have
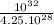 = 0.235.
= 0.235.
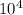 = 2.35.
= 2.35.
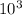
From this, we know that 50 solar masses is greater than the small, massive object found. So, this object can be a single, ordinary star.