Answer:
![[A]_(eq)=0.11M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ww73ras0xz71asazb0gsb9x8x71x2jvrfi.png)
![[B]_(eq)=0.21M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/50kxwini57ees5jlqby5htxog1l83a5vt4.png)
![[C]_(eq)=0.19M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/uyipg13i2ycici855fyplwcj201txz94zq.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, for the given reaction, based on the information about its Gibbs free energy, we obtain the equilibrium constant as shown below:
![Kc=exp(-(\Delta _RG )/(RT) )=exp[-(-5240J/mol )/((8.314J/mol*K)(298.15K)) ]=8.28](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/881bapimg7njryiw8db4j9p3785kmrg1k6.png)
Now, by means of the law of mass action in terms of the undergoing change
 due to the chemical reaction, we obtain:
due to the chemical reaction, we obtain:
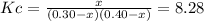
For which the solution for
 by solver is:
by solver is:
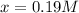
Thus, the equilibrium concentrations result:
![[A]_(eq)=0.3M-0.19M=0.11M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/gytfu78ie4ajx128tdffmm2oxnkqv6emle.png)
![[B]_(eq)=0.4M-0.19M=0.21M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/oc60m8f1rrnzlz4kvwc49wz85pqx79b6h3.png)
![[C]_(eq)=0.19M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/uyipg13i2ycici855fyplwcj201txz94zq.png)
Best regards.