76.703 kPa is the pressure if a sample occupies 68.0 mL at 40.0 C and 95.0 kPa and cooled to -20 degrees while volume remains constant.
Step-by-step explanation:
Volume of the gas V1 = 68 ml
Temperature of the gas T1=40 degrees or 313.15 K
Pressure of the gas P1 = 95 Kpa OR 0.937 atm
Final temperature of the gas T2 = -20 Degrees OR 253.15 K
volume = 68 ml
Pressure P2 = ?
FROM THE FORMULA OF GAS LAW:
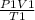 =
=
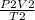
volume is constant so, omitting volume values of temperature and pressure is put in the equation:
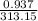 =
=
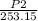
P2 =
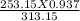
P2 = 0.757 atm or 76.703 kPa is the pressure of the gas when cooled at -20 degrees.