Answer:
Yes they are
Explanation:
In the triangle JKL, the sides can be calculated as following:
=> JK =
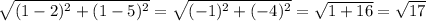
=> JL =
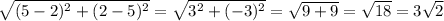
=> KL =
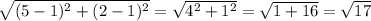
In the triangle QNP, the sides can be calculate as following:
=> QN =
![\sqrt{[-3-(-4)]^(2) + (0-4)^(2) } = \sqrt{1^(2)+(-4)^(2) } = √(1+16)=√(17)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/cad7fgs4tf2ujaukqbfx1p8p23yntcmnto.png)
=> QP =
![\sqrt{[-7-(-4)]^(2) + (1-4)^(2) } = \sqrt{(-3)^(2)+(-3)^(2) } = √(9+9)=√(18) = 3√(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/jyehufsrcfo3dqa83fc84we688g7kmlj6z.png)
=> NP =
![\sqrt{[-7-(-3)]^(2) + (1-0)^(2) } = \sqrt{(-4)^(2)+1^(2) } = √(16+1)=√(17)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/e0c2deyb4ourli3eljawvoqew58ablcu7r.png)
It can be seen that QPN and JKL have: JK = QN; JL = QP; KL = NP
=> They are congruent triangles