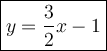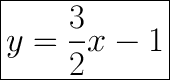
Start with the slope-intercept formula.
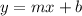
In this formula,
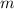 is the slope and
is the slope and
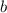 is the y-intercept.
is the y-intercept.
Substitute in the slope.
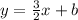
Substitute in the y-intercept.
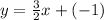
Adding a negative number is the same as subtracting the absolute value of that same number.
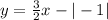
Find the absolute value.