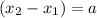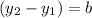Answer:
Given a triangle ABC, Pythagoras' Theorem shows that:
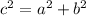
Thus,
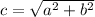
The distance formula, gives an equivalent expression based on two points at the end of the hypotenuse for a triangle.
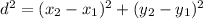
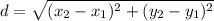
Therefore when given the hypotenuse with endpoints at
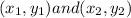
We know that the third point of the right triangle will be at
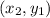
and that the two side lengths will be defined by the absolute values of: