Answer: The pressure equilibrium constant for the reaction is 1473.8
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
Initial partial pressure of methane gas = 2.4 atm
Initial partial pressure of water vapor = 3.9 atm
Equilibrium partial pressure of hydrogen gas = 6.5 atm
The chemical equation for the reaction of methane gas and water vapor follows:
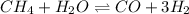
Initial: 2.4 3.9
At eqllm: 2.4-x 3.9-x x 3x
Evaluating the value of 'x':
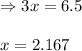
So, equilibrium partial pressure of methane gas = (2.4 - x) = [2.4 - 2.167] = 0.233 atm
Equilibrium partial pressure of water vapor = (3.9 - x) = [3.9 - 2.167] = 1.733 atm
Equilibrium partial pressure of carbon monoxide gas = x = 2.167 atm
The expression of
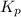 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
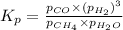
Putting values in above equation, we get:
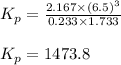
Hence, the pressure equilibrium constant for the reaction is 1473.8