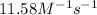Answer: The rate constant at 56°C is
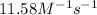
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate rate constant at two different temperatures of the reaction, we use Arrhenius equation, which is:
![\ln((K_(56^oC))/(K_(-8^oC)))=(E_a)/(R)[(1)/(T_1)-(1)/(T_2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/s2a44hyqv90ur2rlflk1zzk4aacd8vc2o7.png)
where,
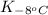 = equilibrium constant at -8°C =
= equilibrium constant at -8°C =
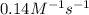
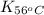 = equilibrium constant at 56°C = ?
= equilibrium constant at 56°C = ?
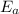 = Activation energy = 50.0 kJ/mol = 50000 J/mol (Conversion factor: 1 kJ = 1000 J)
= Activation energy = 50.0 kJ/mol = 50000 J/mol (Conversion factor: 1 kJ = 1000 J)
R = Gas constant = 8.314 J/mol K
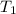 = initial temperature =
= initial temperature =
![-8^oC=[273-8]K=265K](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7nafe03cyyy516r10b3eqeswjc5bpt5whn.png)
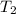 = final temperature =
= final temperature =
![56^oC=[273+56]K=329K](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7pfw361ermxqruk4g1ilavv1l1l5qb0cef.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![\ln((K_(56^oC))/(0.14))=(50000J)/(8.314J/mol.K)[(1)/(265)-(1)/(329)]\\\\K_(56^oC)=11.58M^(-1)s^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7dfglwzzrn3aur308alr7ad3iowedu8e0x.png)
Hence, the rate constant at 56°C is