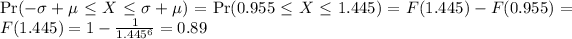Answer:
See detailed explanation.
Explanation:
a) Recall that if a function is a pdf, then it must happen that
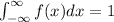 . Then,
. Then,
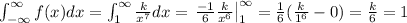
which gives as k = 6.
b). Recall that
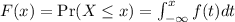 Then, F(x) =0 if
Then, F(x) =0 if
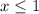 . Then if x>1 we have from the previous point that
. Then if x>1 we have from the previous point that
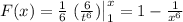
c). We want to know
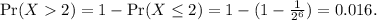
The case
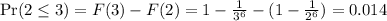
d). We have that
![\mu = \text{E}(X), \sigma = \sqrt[]{\text{E}(X^2)-\text{E}(X)^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/77to2hv5ez28bpve9a79ycg8aiot17tvt6.png) . Where,
. Where,
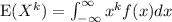
Then,
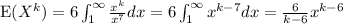
If k<6, then
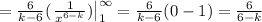
So, the mean (k=1) is 6/(6-1) = 6/5= 1.2 . And the standard deviation is
![\sqrt[]{(6)/(6-2)-1.2^2}= \sqrt[]{1.5-1.2^2} = 0.245](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/q8nespqgujldib2pht19rjvlfjca922ulh.png) .
.
e. We are asked for
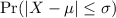 Which is equivalent to
Which is equivalent to