Answer:
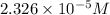 the concentration of iron(III) chloride contaminant in the original groundwater sample.
the concentration of iron(III) chloride contaminant in the original groundwater sample.
Step-by-step explanation:
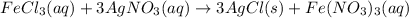
Mass of silver chloride = 2.5 mg = 0.0025 g
1 mg = 0.001 g
Moles of silver chloride =
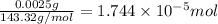
According to reaction, 3 moles of silver chloride are obtained from 1 mole of ferric chloride, then
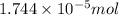 od silver chloride will be obtained from ;
od silver chloride will be obtained from ;
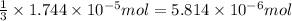 of ferric chloride
of ferric chloride
Volume of the ground water sample = 250 mL= 0.250 L
1 mL = 0.001 L
Concentration of iron(III) chloride =
![[FeCl_3]=(5.814* 10^(-6) mol)/(0.250 L)=2.326* 10^(-5) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ubaasbp06f5ft9hm9i1dl784t2yd7yq9h1.png)
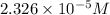 the concentration of iron(III) chloride contaminant in the original groundwater sample.
the concentration of iron(III) chloride contaminant in the original groundwater sample.