Answer:
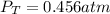
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, it is convenient to rewrite the chemical reaction considering the COCl₂ as the reactant, so we must invert the equilibrium constant as shown below:
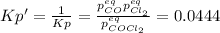
Thus, by introducing the change
 due to reaction's progress, one obtains:
due to reaction's progress, one obtains:
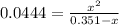
Solving for
 via quadratic equation or solver, one obtains:
via quadratic equation or solver, one obtains:
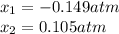
Clearly, the solution is
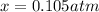 for which the total pressure at equilibrium is:
for which the total pressure at equilibrium is:
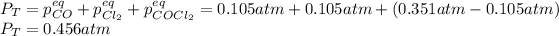
Best regards.