Answer:
The resistance of the axon is
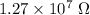 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Inner diameter of the model of an axon,
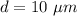
Radius of the model,
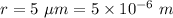
Resistivity of the fluid inside the tube wall,
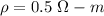
Length of the axon, l = 2 mm = 0.002 m
We know that the resistance in terms of resistivity of an object is given by :
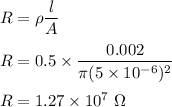
So, the resistance of the axon is
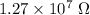 . Hence, this is the required solution.
. Hence, this is the required solution.