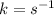The given question is incomplete. The complete question is :
For the net reaction:
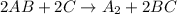 , the following slow first steps have been proposed.
, the following slow first steps have been proposed.
A.
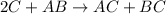
B.
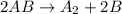
C.
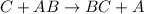
D.
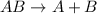
Determine the units of the rate constant for all four reactions listed in the problem above, and enter the correct choices from the list below. Enter 4 letters in order (e.g. ABCD or CBED)
a.
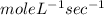
b.
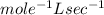
c.
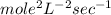
d.
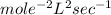
e. None of the above.
Answer: A.
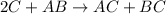 :
:
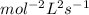
B.
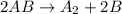 :
:
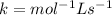
C.
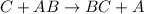 :
:
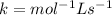
D.
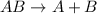 :
:
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
1.
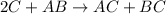
![Rate=k[C]^2[AB}^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/r94s628kh6csslyjfkhxhqoe864s10e4c9.png)
![molL^(-1)s^(-1)=k[molL^(-1)]^2[molL^(-1)}^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/1eoqg1avrwlwtxfxyc1yrw6gt5kp9u4k37.png)
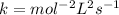
2.
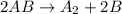
![Rate=k[AB]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/1l3pxtjnjofs0pb4d8risb6k8haeue9im9.png)
![molL^(-1)s^(-1)=k[molL^(-1)]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/yd472b5ta9or508re0r2c3jd8ftyxd6ylh.png)
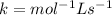
3.
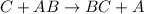
![Rate=k[C}^1[AB]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/cohbn2922vgsc24axkcc9drf7q75z8pzxt.png)
![molL^(-1)s^(-1)=k[molL^(-1)]^1[molL^(-1)]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/n8819z06h91goeeu7oagfuvqlvds0luxr2.png)
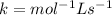
4.
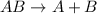
![Rate=k[AB]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/plh6ajpd99r2oxq5ye67ciql545ixm0yu3.png)
![molL^(-1)s^(-1)=k[molL^(-1)]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/bjx1n2fnjp70xufsygcy0nzga6gt380e0q.png)