Answer:
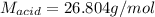
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, by knowing that the used NaOH equals in moles the acid (monoprotic) as shown below, during the titration:
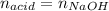
By knowing the volume and the concentration of the NaOH, one obtains:
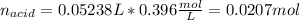
Thus, the molar mass of the acid is computed based on the previously computed moles and the given mass as follows:
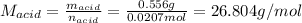
Best regards.