Answer:
When pH = 9.50 ; Volume = 14.8 L
When pH = 4.70 ; Volume = 4.51 L
Step-by-step explanation:
We all know that:
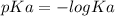
So let us first calculate the pKa values of the following Ka:
Given that:
Ka1 = 1.0×10⁻³
Ka2 = 5.0×10⁻⁸
Ka3 = 2.0×10⁻¹²
For
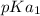 ; we have
; we have
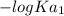
=
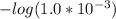
= 3.00
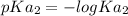
=
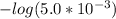
= 7.30
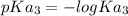
=
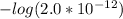
= 11.70
At pH = 4.70:
The pH (4.70) is closer to
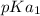 than
than
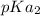 and
and
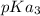 .
.
However, the only important pKa for the dissociation of the acid will be directed towards only
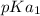
So: At pH = 4.70
-log
![[H_3O^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/le8croj6vie7g8ce25juw9yh73c1whh6bb.png) = pH = 4.70
= pH = 4.70
![[H_3O^+] = 10^(-4.70)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/jbiah7dvhp7kjutz3lqobeppd2q88amowg.png)
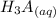

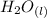 ⇄
⇄
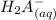

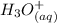
![Ka_1= ([H_2A^-][H_3O^+])/([H_3A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7e49lglcm1dcxct4kcp818m2u7n2wisnwd.png)
![1.0*10^(-3)= ([H_2A^-][H_3O^+])/([H_3A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/tu5oplm8icr7ttd8qvpnzlyf431i6drr19.png)
![(1.0*10^(-3))/([H_3O^+])= ([H_2A^-])/([H_3A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7rqdxtnquah2gy04t7xaoo5t5nbmed99d8.png)
where;
![[H_3O^+] = 10^(-4.70)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/jbiah7dvhp7kjutz3lqobeppd2q88amowg.png)
so, we have:
![(1.0*10^(-3))/([10^(-4.70)])= ([H_2A^-])/([H_3A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/16g8j19rf6vq599vo78vuuq1xjnn0lnqqx.png)
![([H_2A^-])/([H_3A])= 10^(1.7)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/awzlsh3395wj2pc3b0j53klpg1e4rkgbh9.png)
![([H_2A^-])/([H_3A])= 50.12](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/dc24gvk1adajea6ih5hhk9ktb4ni635e1s.png)
Given that;
283.0 mL of
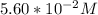 solution is given:
solution is given:
Then ; 283.0 mL = 0.283 L
However;
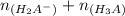 =
=
= 0.013328
=
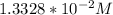
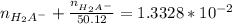
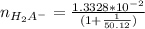
= 0.01307 mole
moles of NaOH required to convert
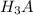 to
to
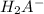 i.e
i.e
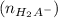
=
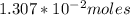
Finally; the volume of NaOH required =
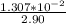
= 0.004507
= 4.51 mL
When pH = 4.70 ; Volume = 4.51 L
When pH = 9.50
We try to understand that the average of
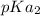 and
and
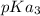 yields 9.50
yields 9.50
i.e
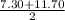
=
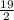
= 9.50
Here; virtually all,
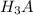 is in
is in
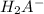 form;
form;
SO; the moles of NaOH required to convert
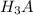 to
to
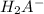 will be:
will be:
= 2 × initial
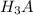 = volume of NaOH × 1.8 M
= volume of NaOH × 1.8 M
= 2 × 1.3328 × 10⁻² mol = Volume of NaOH × 1.8 M
Volume of NaOH =
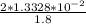
= 0.1481 L
= 14.8 L
When pH = 9.50 ; Volume = 14.8 L