Answer:
The ΔG° for the dissolution of AgCl solid is 55.7 kJ/mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
The Gibbs free energy of the reaction is given by :
![\Delta G_(rxn)^o=\sum[\Delta G^o_(f)]_(products)-\sum[\Delta G^o_(f)]_(reactants)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/o8ewl4q6w10q0b84shaidibhyie34uhb8i.png)
So for reaction :
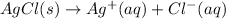
Gibbs free energy of formation of silver ions =
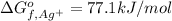
Gibbs free energy of formation of chloride ions =
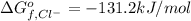
Gibbs free energy of formation of silver chloride solid=
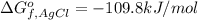
The Gibbs free energy of the reaction of dissolution of AgCl :
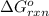 :
:
![\Delta G_(rxn)^o=[77.1 kJ/mol+(-131.2 kJ/mol)]-[-109.8 kJ/mol]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/35wk08e2ld9eeq76ouprdyph3plbkreguu.png)
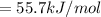
The ΔG° for the dissolution of AgCl solid is 55.7 kJ/mol.