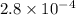The question is incomplete, here is the complete question:
Iron(III) oxide and hydrogen react to form iron and water, like this:
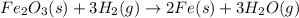
At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 5.4 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of iron(III) oxide, hydrogen, iron, and water at equilibrium has the following composition:
Compound Amount
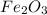 3.54 g
3.54 g
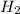 3.63 g
3.63 g
Fe 2.37 g
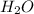 2.13 g
2.13 g
Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits
Answer: The value of equilibrium constant for the given reaction is
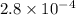
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the molarity of solution, we use the equation:
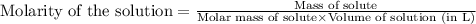
Given mass of hydrogen gas = 3.63 g
Molar mass of hydrogen gas = 2 g/mol
Volume of solution = 5.4 L
Putting values in above equation, we get:
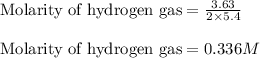
Given mass of water = 2.13 g
Molar mass of water = 18 g/mol
Volume of solution = 5.4 L
Putting values in above equation, we get:
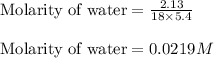
The given chemical equation follows:
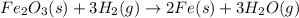
The expression of
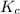 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
![K_c=([H_2O]^3)/([H_2]^3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/gwtz6ns8bpax20vkd1qtqnvu912sxxci5m.png)
The concentration of pure solids and pure liquids are taken as 1 in equilibrium constant expression. So, the concentration of iron and iron (III) oxide is not present in equilibrium constant expression.
Putting values in above equation, we get:
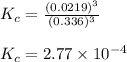
Hence, the value of equilibrium constant for the given reaction is