Answer:
a) Q = 80,000 cal
b) Q = 100,000 cal
c) Q = 540,000 cal
d) Q = 720,000 cal
Step-by-step explanation:
a)1 kg from 0⁰ Ice to 0⁰ water, the heat produced is latent heat of fusion
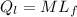 = 1 * 80
= 1 * 80
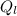 = 80 kCal = 80,000 cal
= 80 kCal = 80,000 cal
b) 1 kg of O°C ice water to 1 kg of 100°C boiling water
Specific heat capacity, c = 1000cal/kg.C
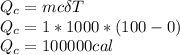
c) 1 kg of 100°C boiling water to 1 kg of 100°C steam
Latent heat of vaporization is needed for this conversion
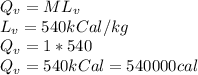
d) 1 kg of O°C ice to 1 kg of 100°C steam.
Q =
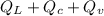
Q = 80,000 + 100,000 + 540,000
Q = 720,000 cal