Answer:
0.00 g
Step-by-step explanation:
We have the masses of two reactants, so this is a limiting reactant problem.
We will need a balanced equation with masses, moles, and molar masses of the compounds involved.
1. Gather all the information in one place with molar masses above the formulas and masses below them.
Mᵣ 30.07 32.00
2CH₃CH₃ + 7O₂ ⟶ 4CO₂ + 6H₂O
Mass/g: 1.50 11.
2. Calculate the moles of each reactant
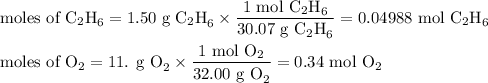
3. Calculate the moles of CO₂ we can obtain from each reactant
From ethane:
The molar ratio is 4 mol CO₂:2 mol C₂H₆
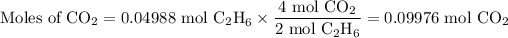
From oxygen:
The molar ratio is 4 mol CO₂:7 mol O₂
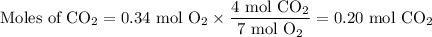
4. Identify the limiting and excess reactants
The limiting reactant is ethane, because it gives the smaller amount of CO₂.
The excess reactant is oxygen.
5. Mass of ethane left over.
Ethane is the limiting reactant. It will be completely used up.
The mass of ethane left over will be 0.00 g.