The question is incomplete, complete question is:
A solution containing CaCl2 is mixed with a solution of Li2C2O4 to form a solution that is
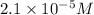 in calcium ion and
in calcium ion and
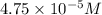 in oxalate ion. What will happen once these solutions are mixed?
in oxalate ion. What will happen once these solutions are mixed?
Answer:
On mixing of both the solutions no precipitation will occur due to lower value of an ionic product of calcium oxalate from its solubility product.
Step-by-step explanation:
Molar concentration of calcium ions =
![[Ca^(2+)]=2.1* 10^(-5) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/h9yazi1vvym5qw2ktcxd9ioxgax86t7koq.png)
Molar concentration of oxalate ions =
![[C_2O_4^(2-)]=4.75* 10^(-5) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/enmxv1kehqnzkbi3gm3zwd5jzse7gbv2mc.png)
ionic product of calcium oxalate in solution :
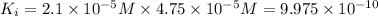
Solubility product of calcium oxalate =
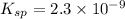
Generally precipitation occurs when ionic product of substance in solution exceeds its solubility product.
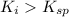 (precipitation occurs)
(precipitation occurs)
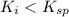 (non precipitation occurs)
(non precipitation occurs)
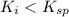
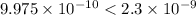
On mixing of both the solutions no precipitation will occur due to lower value of an ionic product of calcium oxalate from its solubility product.