Answer:
using bond energies = - 37 kJ
using enthalpies of formation = - 45.7 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
From the reaction;
CH2═CH2(g) + H2O(g) -------> CH3CH2OH(g)
From the above reaction; there are 4 (C-H) bonds , 1 ( C=C) and 2 (H-O) of ethene which forms 5(C-H) bonds, 1 (C-C) and 1 (C-O) and 1(H-O) bonds.
Using Bond Energies; the heat of the reaction can be written as:
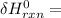 ∑ energy of old bond breaking + ∑ energies of the new bond formation.
∑ energy of old bond breaking + ∑ energies of the new bond formation.
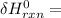 ∑
∑
![[(4 * BE_(C-H)) + BE_(C-C)) + + BE_(O-H))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/f452jvnhctafdaqiawdb46y4m5rdrqtonw.png) + ∑
+ ∑
![[(5 * BE_(C-H)) + BE_(C-C)) + BE_(O-H)+ BE_(C-O))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/faoncuxcr6y3fk69mzgy0ux8x52kb3mqd2.png)
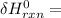 ∑
∑
![[4*413 kJ)+(614kJ)+(2*647kJ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/td62lwptc5w3y3gtjvut40e6bkge6lk0kt.png) + ∑
+ ∑
![(5*-413kJ)+(-347kJ)+(-467kJ)+(-358kJ)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/63zhkzawz27wvkr5385m5vd489pq8ka8yb.png)
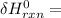 -37 kJ
-37 kJ
To calculate the heats of reaction by using enthalpies of formation; we have:
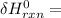 ∑
∑
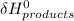 - ∑
- ∑
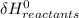
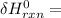 ∑
∑
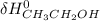 - ∑
- ∑
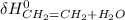
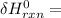 (-235.1 kJ) - [(+52.47 kJ) + (-241.826 kJ)]
(-235.1 kJ) - [(+52.47 kJ) + (-241.826 kJ)]
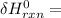 -45.7 kJ
-45.7 kJ