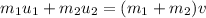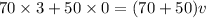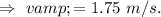Answer:
When a particle or a system of particles move in a system where no external force acts, then the total linear momentum of the particle system remains constant.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data:
Total mass of the skateboarder,
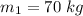
Mass of the friend,
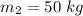
Initial velocity of the skateboarder,
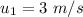
Initial velocity of the the friend,
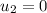
Let the new velocity of the skateboarder when his friend jumps be
 .
.
From the conservation law of linear momentum,