Step-by-step explanation:
The integrated first law is given by :
![[A]=[A]_o* e^(-k* t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/lugq61kawpuxkucfphf58ssm1bxt0zo430.png)
Where:
![[A]_o](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/4pmjkus4n3cfntqcbgc1rjdz49krp7grr3.png) = initial concentration of reactant
= initial concentration of reactant
[A] = concentration of reactant after t time
k = rate constant
a)
![[A_o]=x](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/xjfebupkio8l77x1aeln6ewhrumigwqcm6.png)
![[A]=(x)/(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/tq974nobo0l2k4zg18238zv5k9rn4l46ox.png)
t = 1000 s
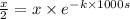
Solving for k:
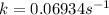
The rate constant for this reaction is
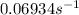 .
.
b)
![[A_o]=0.67 mol/L](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5d9ct18b1pp87rz5kv7js1iaecy66474cr.png)
![[A]=0.53 mol/L](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ekqrdeknqu19od1bbp25bil9nwi3o1ujv3.png)
t = 25 s
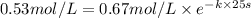
Solving for k:
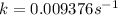
The rate constant for this reaction is
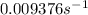 .
.
c) 2 A → B +C
![[A_o]=0.153 mol/L](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/3i3f1nrh9jujvz4qbacnnjfb96fupl55yn.png)
![[A]=?](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/oghjv7nqreoebvu50bk4s0gmrm7i7qo3q0.png)
![[B]=0.034 mol/L](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/2bpjrfyakk8qmbsxt0r77xi2oo3xeyi182.png)
According to reaction, 1 mole of B is obtained from 2 moles of A.
Then 0.034 mole of B will be obtained from:
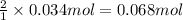 of A
of A
So, the concentration left after 115 seconds:
![[A]=0.153 mol/L-0.068 mol/L=0.085 mol/L](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/60uz9wkws20b7qizywf8gc4qczm9g07i3d.png)
t = 115 s
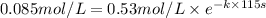
Solving for k:
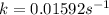
The rate constant for this reaction is
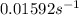 .
.