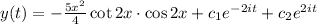Answer:
So, solution of the differential equation is
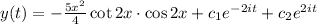
Explanation:
We have the given differential equation: y′′+4y=5xcos(2x)
We use the Method of Undetermined Coefficients.
We first solve the homogeneous differential equation y′′+4y=0.
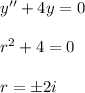
It is a homogeneous solution:
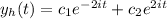
Now, we finding a particular solution.

we get
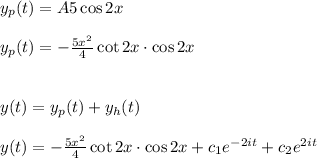
So, solution of the differential equation is