Answer:
The dissociation constant for the acid ( experimental ) is 1.45 lit/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
The value of dissociation constant can be calculated as,
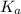 = C × ∝²
= C × ∝²
Where, C = concentration of the solution = 0.329M
∝ = Degree of dissociation
again , Degree of dissociation can be obtained form :
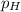 = C × ∝
= C × ∝
∝ =
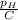
∝ =
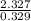 = 7.072
= 7.072
So, now
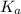 = C × ∝²
= C × ∝²
= 0.329 ×( 7.072)²
= 1.45 lit/ mol