Answer: The enthalpy of the reaction is 269.4 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the heat absorbed by the calorimeter, we use the equation:
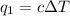
where,
q = heat absorbed
c = heat capacity of calorimeter = 675 J/°C
 = change in temperature =
= change in temperature =
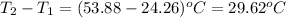
Putting values in above equation, we get:
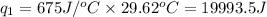
To calculate the heat absorbed by water, we use the equation:
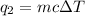
where,
q = heat absorbed
m = mass of water = 925 g
c = heat capacity of water = 4.186 J/g°C
 = change in temperature =
= change in temperature =
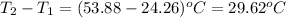
Putting values in above equation, we get:
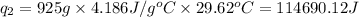
Total heat absorbed =
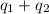
Total heat absorbed =
![[19993.5+114690.12]J=134683.62J=134.7kJ](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/1i0oam59a5ujkcgtj3qd3pkk0h24xlf3ur.png)
To calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction, we use the equation:
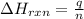
where,
q = amount of heat absorbed = 134.7 kJ
n = number of moles of hydrocarbon = 0.500 moles
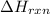 = enthalpy change of the reaction
= enthalpy change of the reaction
Putting values in above equation, we get:
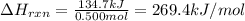
Hence, the enthalpy of the reaction is 269.4 kJ/mol