Answer:
9.07
Step-by-step explanation:
We have to start with the buffer system reaction, so:
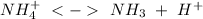
When we have the hydrochloric acid (a strong acid) the
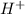 of the hydrochloric acid (
of the hydrochloric acid (
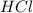 ) will interact with the base of the buffer system (
) will interact with the base of the buffer system (
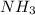 ) to produce more acid (
) to produce more acid (
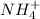 ), so:
), so:
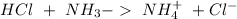
Therefore the concentration of
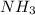 will decrease and the concentration of
will decrease and the concentration of
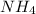 will increase. The next step then would be the calculation of the moles of the acid and base in the buffer system. So:
will increase. The next step then would be the calculation of the moles of the acid and base in the buffer system. So:
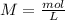
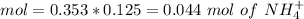
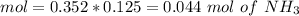
If we add 0.02 mol of
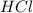 we can calculate the amount of acid and base that changes in the buffer system.
we can calculate the amount of acid and base that changes in the buffer system.
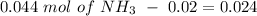
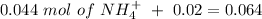
Now, we can calculate the concentration of each species if we divide by the number of moles:
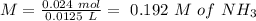
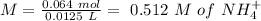
If we use the hendersson hasselbach equation we can calculate the pH value again:
![pH=p{ K }_( a )+log(\frac { { [A }^( - )] }{ [HA] } )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/u5su7eblgr3yieo31yv9lgcp2m8bmfdgkq.png)
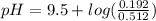
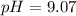
The final pH value is 9.07