Answer:
86.53 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Mass of clay (m) = 14.0 g = 0.014 kg
Mass of block (M) = 110 g = 0.110 kg
Initial speed of block (U) = 0 m/s
Sliding distance (d) = 7.50 m
Coefficient of friction between block and surface (μ) = 0.650
Let the initial speed of clay be 'u' and speed of clay and block just after collision be 'v'.
Now, momentum is conserved just before and just after collision.
Momentum just before collision =
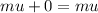
Momentum just after collision =
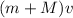
Therefore,
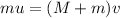 --------- (1)
--------- (1)
Now, using newton's second law and we find the acceleration of the system.
The frictional force is given as:
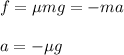
Now, using equation of motion, we can find the velocity just after collision.
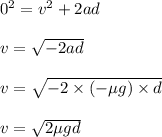
Plug in the given values and find 'v'. This gives,
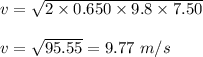
Now, using equation (1) and substituting the given values, we get:

Therefore, the speed of the clay immediately before impact is 86.53 m/s.