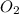The 2 decomposition reactions are:
B.
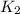
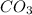 (s) -->
(s) -->
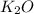 (s) +
(s) +
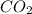 (g)
(g)
C.
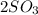 (g) -->
(g) -->
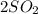 (g) +
(g) +
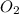 (g)
(g)
Step-by-step explanation:
Step 1:
A decomposition reaction is one in which a single compound breaks down into two or more products.
Step 2:
Let us examine each reaction if it satisfies the above rule.
A. 2 LiOH +
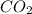 --->
--->
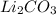 +
+
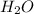
In this reaction we have 2 reactants giving 2 products. Hence this is not a decomposition reaction.
B.
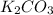 --->
--->
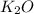 +
+
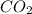
In this reaction a single reactant potassium carbonate gives rise to 2 products Potassium Oxide and carbon-di-oxide. Hence this is a decomposition reaction
C.
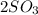 --->
--->
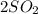 +
+
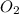
In this reaction a single reactant sulfur tri-oxide gives rise to 2 products sulfur di-oxide and oxygen. Hence this is a decomposition reaction.
D.
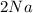 +
+
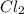 --->
--->
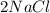
In this reaction 2 reactants sodium and chlorine gives rise to a single product sodium chloride. Hence this is not a decomposition reaction.
Step 3:
Answer:
The 2 decomposition reactions are:
B.
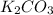 (s) --->
(s) --->
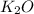 (s) +
(s) +
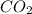 (g)
(g)
C.
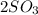 --->
--->
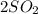 +
+